Virus
What is a Pharming Attack? How to Protect Yourself Online
Learn what a pharming attack is, how it works, and why it’s a growing online threat. Discover expert tips to protect yourself & your data today!🛡️💻

In today’s digital age, online security has become more critical than ever. Even the most watchful internet users might become targets of assaults due to the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
Pharming attacks are such hazardous and cunning threats. Unlike phishing, which relies on tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information, pharming manipulates the very foundation of internet browsing to lead users to fraudulent websites.
What a pharming assault is, how it operates, and—above all—how to avoid being a victim of this online threat are all covered in this essay.
What is a Pharming Attack?
Pharming attacks are a type of cybercrime in which criminals secretly divert consumers from trustworthy websites to phony ones.
This is done by manipulating the DNS (Domain Name System) or infecting a user’s device with malicious software.
Imagine putting “www.yourbank.com” into your browser and being sent to a bogus site that appears just like your bank’s homepage.
You input your login credentials, believing you are secure, yet the information is promptly taken. This is how pharming targets unwary consumers.
What Are the Different Types of Pharming?
Pharming attacks typically fall into two categories:
- DNS Cache Poisoning: This method targets the DNS servers that translate domain names into IP addresses. Without changing the actual website URLs, attackers can reroute visitors to fraudulent websites by corrupting the DNS cache.
- Malware-Based Attacks: By altering a victim’s local DNS settings with malicious software, attackers can redirect their internet traffic to phony domains.
Despite the different approaches, both types aim to deceive users into divulging sensitive information like login credentials, credit card details, or personal data.
Why Are Pharming Attacks So Dangerous?
Pharming attacks are particularly insidious because they can occur without a user’s awareness. Unlike phishing scams that rely on obvious email or message bait, pharming silently redirects users.
The consequences of pharming can be severe:
- Stolen Credentials: Attackers can capture sensitive information, including usernames, passwords, and financial details.
- Financial Losses: Victims may unknowingly transfer money or make purchases on fraudulent platforms.
- Erosion of Trust: Pharming undermines user confidence in online transactions and internet safety.
How Does a Pharming Attack Work?
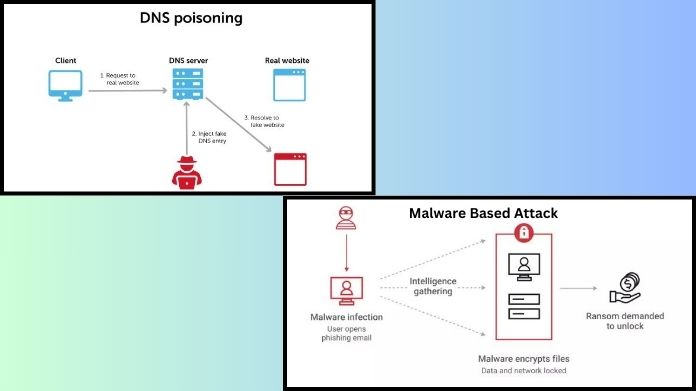
Pharming is a sophisticated kind of fraud in which internet users are directed to false websites in order to gain personal or financial information such as login passwords, credit card data, or social security numbers.
While pharming can take numerous forms, it is often carried out using one of the following techniques:
1. DNS Cache Poisoning:
DNS servers act as the internet’s address book, converting domain names into IP addresses. Attackers can reroute legal traffic to fraudulent websites by inserting malicious data into a DNS server’s cache.
This technique is known as DNS cache poisoning. Imagine someone in a phone book changing the address; you believe you’re contacting a friend, but it turns out to be a fraudster.
2. Malware-Based Attacks:
In this type, attackers deploy malware to alter a user’s DNS settings locally. Once infected, the device consistently redirects traffic to fake sites, even if the user types the correct URL.
Phishing emails, malicious downloads, and hacked websites are common ways for malware to spread.
Realtime Examples of Pharming Attacks
- 2007 Pharming Attack in Brazil: Attackers targeted Brazilian banks by compromising local DNS servers. This large-scale attack redirected users to fake banking websites, leading to significant financial losses for many victims.
- Chinese Pharming Incident (2010): Chinese internet users attempting to access popular websites like Google and Facebook were redirected to fraudulent pages due to a DNS cache poisoning attack.
- Pharming Through Malware (Recent Years): Malware such as “Trojan.Qhost” modifies the host file on a user’s device, sending traffic to bogus login pages for services such as PayPal and Amazon. This is still a typical approach for phishing attackers.
These examples highlight the global and ongoing threat of pharming attacks, emphasizing the need for proactive cybersecurity measures.
Common Signs of a Pharming Attack
Recognizing the warning signs of a pharming attack can save you from potential harm:
- Suspicious URLs: Verify URLs again for minor alterations like misspellings or strange domain extensions.
- Unusual Website Behavior: Watch out for discrepancies like unresponsive links, a missing HTTPS padlock, or design inconsistencies on familiar sites.
- Browser Warnings: Heed warnings from your browser about unsafe websites or invalid SSL certificates. These warnings are intended to shield you from efforts at pharming and phishing.
How to Protect Yourself from Pharming Attacks?

Here are practical steps to safeguard your online presence:
- Use Trusted DNS Servers: Opt for reputable DNS providers like Google Public DNS or Cloudflare, which offer enhanced security features.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security to your accounts by enabling 2FA, which requires a second verification step beyond just your password.
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, browser, and security software to patch vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Install Reliable Security Software: Make use of antivirus and anti-malware software that can identify and stop questionable activity, such as pharming efforts.
- Verify URLs: Before entering sensitive information, ensure the URL is correct and starts with “https://” to confirm it’s secure.
- Educate Yourself: To build a more safe online community, keep up with changing cyberthreats and provide friends and family cybersecurity advice.
What to Do If You Suspect a Pharming Attack?
If you think you’ve fallen victim to a pharming attack, take immediate action:
- Disconnect from the Internet: Prevent further data exposure by temporarily cutting off your device’s connection.
- Scan Your Device for Malware: Use trusted security software to detect and remove any malicious programs.
- Notify Your Bank or Service Provider: If sensitive information was compromised, inform the relevant institutions to secure your accounts.
- Report the Incident: Alert local authorities or cybersecurity organizations to help prevent others from becoming victims.
Final Thoughts
Pharming attacks are a growing threat in the digital world, but you don’t have to fall victim to them.
You may safeguard yourself and your private data by being aware of how these threats operate and adhering to online security best practices.
Remember, staying vigilant and proactive is the key to navigating the internet safely. With this information at your disposal, you may browse the internet with assurance and take use of all of its advantages without worrying about anything.
Be careful out there!

















Tenkov
January 28, 2025 at 7:43 am
Very insightful post! Your explanation of pharming attacks and how they differ from phishing is incredibly helpful. I appreciate the detailed prevention tips and security measures to stay safe online. Thanks for sharing such valuable cybersecurity knowledge!